Implement Today – Measure Tomorrow. Top-8 Modern Tracking Functions

Inefficient logistics, poor asset utilisation, safety risks and lack of real-time visibility are some issues relevant to modern manufacturing. These challenges can lead to increased costs, operational delays and missed opportunities.
Now, tracking systems and location detection provide information to help solve these critical business problems. From optimising supply chains to improving personal safety, here are the top 8 modern tracking features that can transform your operations, boost efficiency and deliver measurable results.
Table of contents
Reliable Information Through OSNMA
Comprehensive Activity Tracking
РРР System
PPP (precise point positioning) system is a high-accuracy satellite-based positioning technique widely used in navigation, geolocation, and environmental monitoring. Unlike RTK (real-time kinematics), which relies on relative positioning using multiple reference stations, PPP uses a single receiver and applies precise corrections from satellite data or amendments data centres to achieve higher accuracy.
This capability makes PPP particularly attractive where the use of multiple base stations is impractical or cost prohibitive. That's why a wide range of high-precision applications are possible with PPP, including autonomous navigation and agricultural monitoring.
PPP systems operate globally, making them ideal for applications requiring positioning in remote or inaccessible areas. The process of achieving high accuracy with PPP involves modelling, estimating and applying external corrections. These corrections are delivered to the user via satellite or the Internet. While the initial convergence time to achieve full accuracy can vary, advanced systems can achieve decimeter-level accuracy in less than a minute under optimal conditions.
Where is it used? Precision agriculture. PPP-enabled GPS technology can help improve farming efficiency through automated tractor guidance, soil sampling and mapping, variable rate technology (VRT) and more.
Reliable Information Through OSNMA
The OSNMA (open service navigation message authentication) feature adds an extra layer of reliability to tracking systems. This innovation guarantees that the information received is trustworthy and tamper-proof, bolstering confidence in the data transmitted from point A to point B.
The OSNMA functionality operates through a sophisticated cryptographic framework uses a combination of MACs (message authentication codes) and a one-way chain of keys known as the TESLA protocol.
Each navigation message transmitted by the Galileo satellites contains a MAC and allows the receiver to verify its authenticity. The receiver first demodulates the navigation data together with the corresponding MAC and then retrieves the keys required to authenticate this MAC. This process ensures that only genuine data is used for position calculations.
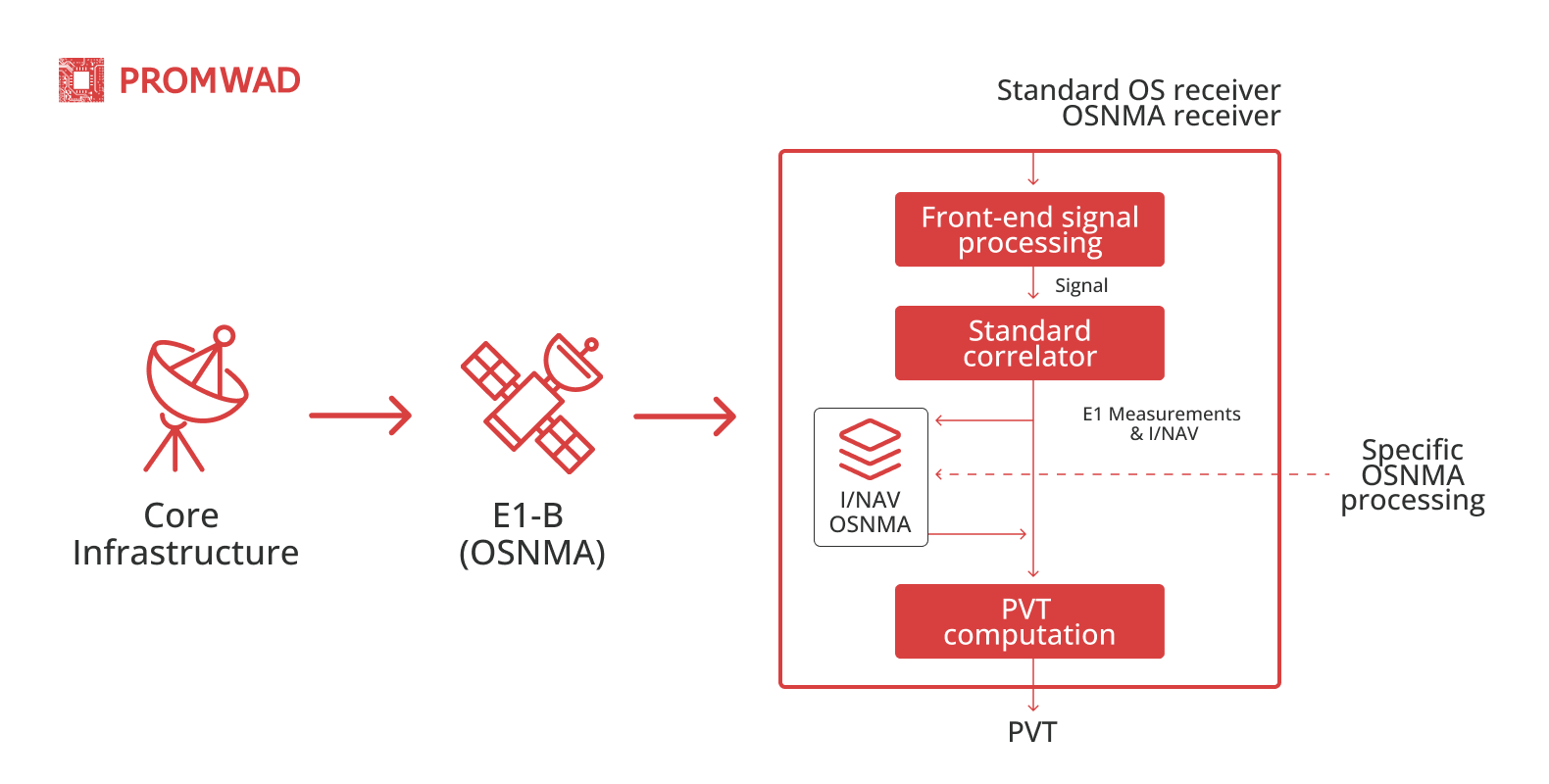
OSNMA scheme
OSNMA requires no additional network connectivity, making it highly accessible and efficient in a variety of environments. It is designed to be fully backward compatible with existing GNSS systems. This means that users can benefit from security without the need for significant hardware or software upgrades.
Moreover, OSNMA is offered free-of-charge to all users of the Galileo Open Service, democratising access to advanced navigation security features.
Where is it used? Drone delivery. Spoofing or tampering with GPS signals can lead to route deviations, delayed deliveries, or theft. By adopting OSNMA, the logistics companies mitigate security risks, builds customer trust, and positions itself as a leader in the drone delivery market.
Comprehensive Activity Tracking
Comprehensive activity tracking meets the demand for detailed health and performance information. Todays fitness trackers are no longer devices that count steps - they are equipped with sensors and algorithms to track a wide range of physiological parameters.
Users want a holistic view of their health to make decisions about their fitness activities and overall well-being. Advanced integration of accelerometers, gyroscopes and optical heart rate monitors is the key to comprehensive activity tracking technology.
Optical sensors can continuously monitor heart rate and provide real-time data. This is essential for optimising training and managing recovery. The data is synced with mobile apps that provide personalised feedback and recommendations based on the user's goals.
As the demand for total activity tracking solutions grows, we can expect further innovation. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will enhance the analytical capabilities of these devices and give deeper insights into user behaviour and health trends. Integrating tracking capabilities into everyday items such as clothing or smart home devices will make it easier for users to monitor their health throughout the day.
Where is it used? Literally everywhere. About one in three American adults use a wearable device, such as a smartwatch or fitness band. By 2023, 45% of respondents in Spain said they owned a smartwatch, with 68% expressing interest in purchasing a new smartwatch for health purposes.
Customisable Sensor Integration
Customisable sensor integration allows you to create bespoke solutions to meet the specific needs of users in a wide range of industries. Today's trackers are designed to connect to accelerometers, gyroscopes, heart rate monitors and environmental sensors.
Users can offer tracking systems that monitor critical metrics related to their activities along with location data. For example, a tracker used by firefighters can be equipped with sensors to monitor vital signs and movement patterns to keep them safe in dangerous environments.
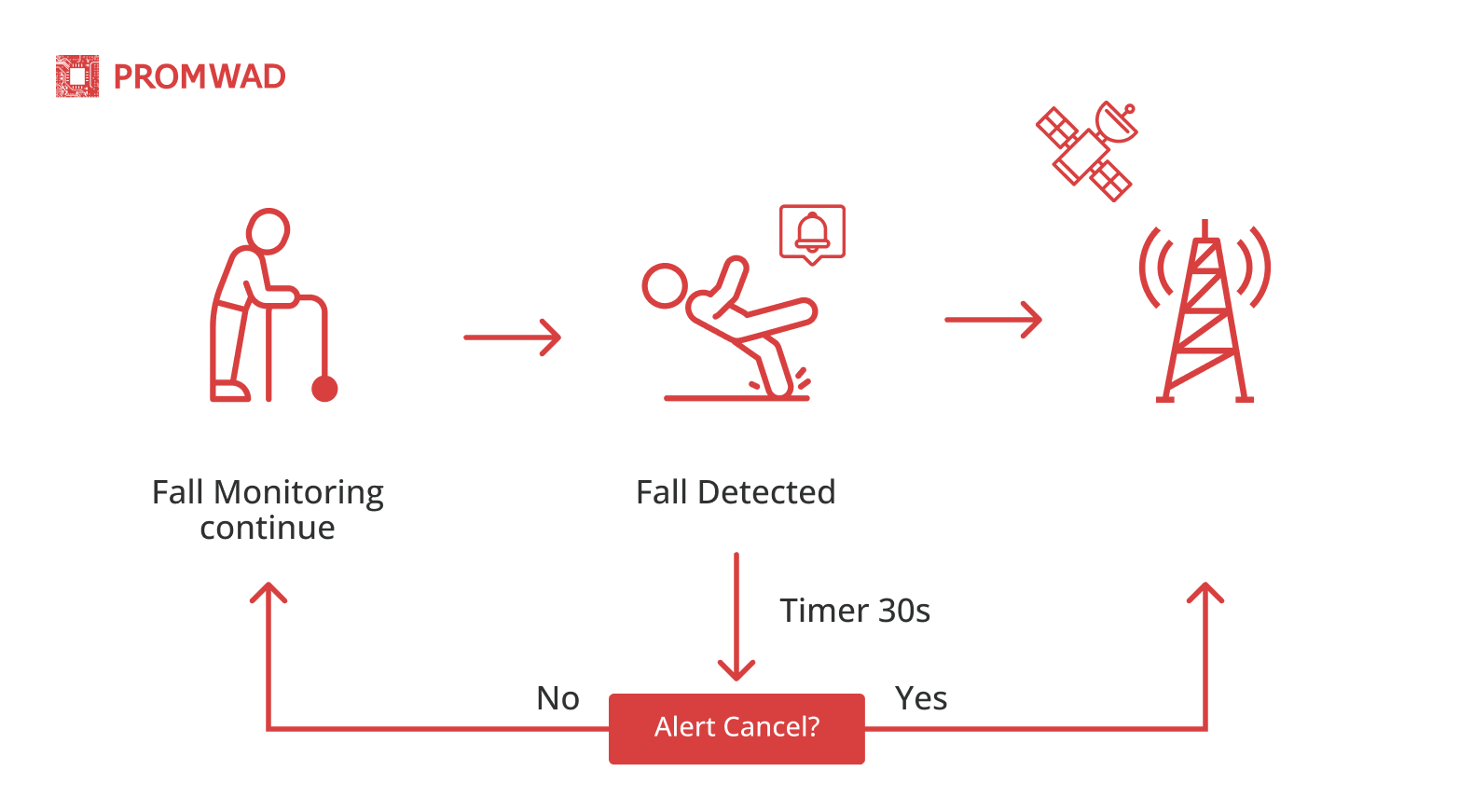
The process of working with the fall detection system
The integration of custom sensors into tracking systems enhances the functionality of these devices. Custom sensors can be designed to operate in extreme environments or to monitor unique assets that standard sensors cannot effectively track. The trend towards the integration of custom sensors is supported by advances in protocols for IoT systems.
As technology advances, customisable sensor integration and modular systems will shape the future of tracking. The continued development of modular sensor systems will allow users to adapt their equipment as their needs change.
Where is it used? Remote patient monitoring systems. For example, patients recovering from heart surgery need sensors to monitor heart rate, blood pressure and blood oxygen saturation. The healthcare provider is alerted in real time, allowing early action on an abnormal condition and adjustment of treatment.
Real-Time Feedback Mechanisms
Real-time feedback mechanisms provide instant alerts and notifications to users to increase their awareness and speed of response to critical situations. For example, in high-risk environments such as construction sites or emergency services, trackers can detect sudden changes in movement patterns or vital signs, instantly sending alerts to both the user and their support team.
The integration of real-time feedback also facilitates a proactive approach to performance management. Users can receive alerts when they cross prohibited areas or when their activity levels unexpectedly drop, prompting them to take corrective action.
As technology advances, the potential for real-time feedback mechanisms in tracking systems will expand. More complex algorithms will continuously analyse user data, providing predictive information to anticipate potential risks before they occur.
Where is it used? Corporate fitness trackers with real-time feedback mechanisms and personalised health metrics, push notifications, reminders and gamification to drive engagement.
Enhanced Security Features
Individuals and companies are becoming more aware of the potential risks associated with tracking devices, leading to a demand for solutions that protect sensitive data.
Real-time location tracking, geo-fencing and strong data encryption have become security-focused trackers' standards. They monitor for unauthorised access and intrusion into secure areas, and users are immediately alerted when tracked assets enter or leave certain areas or when suspicious activity is detected.
The integration of advanced encryption protocols ensures that the data transmitted by the tracker is protected from interception or manipulation. Another important aspect of improving the security of tracking devices is the introduction of strong authentication methods. Trackers now use biometric verification or two-factor authentication. This extra layer of security reduces the risk of sensitive information being leaked.
A specific feature of these devices is the need for regular software updates to address vulnerabilities and protect against new threats, thus maintaining the long-term effectiveness of your tracking system.
Where is it used? This is important for organisations that manage fleets of vehicles or expensive equipment, as it allows them to closely monitor movements and respond quickly to potential theft or unauthorised use; the loss of sensitive data or assets can have significant financial and reputational consequences.
Multi-Variant Geolocation
Multivariant geolocation in trackers uses GPS, WiFi, BLE (Bluetooth low energy), UBW (ultra-wideband) and cellular triangulation technologies for accurate and reliable positioning in various environments. By combining different methods, gadgets provide location tracking for the user, whether outdoors in the countryside or travelling through complex indoor environments.
Example of using a tracker with a stock control application
GPS remains the primary technology for outdoor tracking due to its high accuracy and global coverage. But in urban environments, where GPS signals can be blocked by tall buildings, WiFi and cellular triangulation serve as complementary solutions. WiFi sniffing uses signals from nearby wireless networks to determine location, while cellular triangulation calculates position based on signal strength from multiple cell towers.
BLE and fixed location beacons are used for indoor positioning. BLE beacons transmit signals that trackers use to determine proximity to known reference points. This is particularly useful in warehouse management or retail applications where accurate asset tracking is required. LoRaWAN-based geolocation enables tracking over long distances while minimising power consumption.
UWB is the most advanced technology for indoor navigation, offering centimeter-level accuracy, low latency, and high interference resistance. Unlike Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, UWB enables precise real-time positioning by measuring ToF (time-of-flight) signals. It is perfect for asset tracking, smart access control, and industrial automation in complex environments like warehouses, hospitals, and smart buildings.
As geolocation algorithms and connectivity capabilities improve, the accuracy and efficiency of multi-variant trackers will continue to advance, making trackers smarter and more adaptable to new needs.
Where is it used? Vehicle tracking in a fleet, inventory management in a warehouse or personal security in the city. A practical example is an ECU-based vehicle tracking system designed for high-precision positioning and real-time diagnostics in dense urban environments, such as cargo bike and light vehicle fleets.
Custom Solutions Platform
Perhaps the most exciting development in modern trackers is their evolution into customisable platforms. Users can tailor the functionality of their devices to suit specific tasks or industries. For example, a search and rescue tracker could focus on location and movement patterns in challenging environments.
By integrating advanced sensors and algorithms, these devices can pinpoint a user's location in real time and alert teams if they deviate from their intended path. This capability is critical in emergency situations where every second counts and enables professionals to act quickly and efficiently.
Customisation of the tracking device includes the design of the user interface and the presentation of the data. Users can choose how information is displayed and prioritise indicators based on their preferences or operational needs. A high level of personalisation ensures that users can quickly interpret important data to make decision-making processes more efficient.
As technology advances, the potential for personalised decision platforms in trackers will expand. Future features may include artificial intelligence-based analytics that adaptively learn based on user behaviour and environmental conditions
Where is it used? An oil worker tracker can be configured to monitor environmental hazards such as overheating or gas leaks during a shift, ensuring that worker safety is prioritised in potentially dangerous conditions.
***
The field of tracking development is evolving with customisable platforms, multi-variant geolocation, real-time feedback mechanisms and enhanced security features. As we continue to see the integration of more complex technologies into tracking systems, the potential for innovation is limitless.
Promwad harnesses these trends to develop tracking devices of varying complexity, using a wide range of components to meet your unique requirements. Whether you need a specialised tracker for hazardous environments or a versatile device suitable for a wide range of applications, our team is ready to support you from concept to mass production.
Let's talk about a partnership for innovative tracking solutions!
Our Case Studies in Industrial Design





