
IEEE 1588 PTP
Solutions with IEEE 1588 PTP for Network Switches, Routers, and Infrastructures
We enable the IEEE 1588 PTP support in software and hardware for diverse telecommunication devices. With advanced timestamping capabilities, our custom solutions align the clocks of various network elements with extremely low latency.
How Does It Work?
IEEE 1588 functions by exchanging two-way timing messages between the master and slave clocks. In these messages, the slave receives information about the time the master is on. The delay is easily determined in this process. Subsequently, the protocol estimates the one-way message delay by halving the round-trip delay.

Benefits of IEEE 1588 Synchronisation Protocol
IEEE 1588 synchronisation protocol is essential for coordinating and aligning various components or processes within a system. It provides real-time applications with the following information:
- Precise time-of-day (ToD) information
- Time-stamped inputs
- Scheduled and synchronised outputs
This protocol is the sole standardised terrestrial mechanism for delivering phase/time with the highest accuracy via a packet-based network. Its application areas include mobile networks, industrial process control, audio/video networks, smart energy distribution, transportation, automotive, and IIoT.
How Promwad Adopts This Technology
The model range we employ:
- Ethernet switches: VSC7546TSN, VSC7549TSN, VSC7552TSN, VSC7556TSN, VSC7558TSN
- PHYs/10G PHYs: VSC8572, VSC8574

Software Development
IEEE 1588v2 PTP is integrated as an application-level module within the IStaX SDKs. It operates on Microchip Ethernet switch hardware and is supported by a rewriter, egress port modules, and timing-aware PHYs.
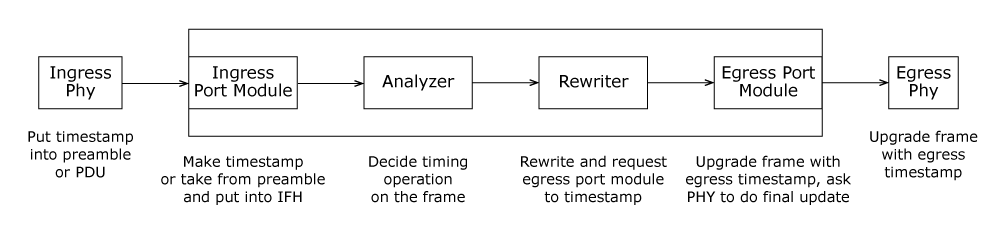
The PTP implementation encompasses the following features:
-
Ordinary and boundary clocks employing basic delay and peer-to-peer mechanisms
-
Peer-to-peer/end-to-end transparent clock
-
Local clock and servo
-
Best Master Clock (BMC) algorithm
By default, the protocol operates over Ethernet PTP using Ethernet multicast. It is possible to configure PTP over IPv4 multicast or unicast.
Supported Applications
PTP synchronisation profiles, introduced in IEEE 1588-2008, facilitate the adoption of PTP by various standards bodies (e.g. ITU-T, IETF, SMPTE, AES, IEC, Avnu, AUTOSAR, LXI, AIA) for specific applications such as financial/enterprise, professional broadcast, power industry, and test and measurement.
Our engineers enable support of the following profiles:
IEEE Std 1588-2019 for generic applications
G8275.1, G.8265.1 for telecom industry
IEEE Std 802.1AS for audio/video, industrial automation, and automotive applications
Our Tech Stack
IEEE 1588-2008 | IEEE 802.1AS-2020 | ITU-T G.8265.1 | ITU-T G.8275.1 | ITU-T G.8275.2 | SMPTE ST-2059-2
PHC | Timestamp unit | Servo | PPS in/out | GNSS | Ordinary clock | Transparent clock | Boundary clock
5G/6G telecom systems | Multimedia broadcasting | Financial trading | Industrial automation
Servo algorithm | two/one-step sync mode | e2e/p2p delay mechanism | l2/l4 transport | SyncE usage | Domain number | PHC time format | Messages timings | BMCA method | Unicast/Multicast
Microchip | Realtek | NVIDIA | Broadcom | linuxptp | PTPd
Our Case Studies in Telecom
Do you want to implement IEEE 1588 functionality for your project?
Please, drop us a line. We will contact you today or next business day. All submitted information will be kept confidential.
FAQ
What are the key areas of implementation for PTP?
How does IEEE 1588 PTP work?
The protocol determines the server and client operating modes, as well as the master and slave parts synchronisation messages. The slave synchronises with the master, which is the source of time. A master synchronised to a time reference, such as GPS or CDMA, is called a grandmaster.
- Master sync messages
- Master delay response messages
- Slave delay request messages
The BMC technique enables several masters to agree upon the best clock for the network in addition to the messages.
At least one master and one slave are needed for synchronisation via LAN. A single master can synchronise with several slaves. The slaves use synchronisation messages from the masters to adjust their local ones. All of them record exact timestamps.








