
MPLS
Solutions
MPLS Solutions in Telecom Network Design Services
We use MPLS within our telecom network design services to establish reliable traffic delivery across various networks. The use of MPLS solutions in network design enables optimised routing and virtual environment creation, enhancing overall network efficiency and flexibility.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a set of rules to control and route the traffic flow between destination addresses. Explore how this protocol can upgrade your network devices with enhanced connectivity in real-time applications.
How Does MPLS Work?
Multiprotocol Label Switching is a packet-forwarding technology that can encapsulate packets of multiple network protocols.
The data transmission to the endpoint is organised via predetermined short-bit sequences or labels, instead of network addresses, which distinguishes this technique from others.
Now, let's explore how this protocol operates. Imagine you’re sending an IP packet from one endpoint to another. Before transmitting the IP packet, a predefined route is established. Along the way, intermediate routers only need to interpret the MPLS labels containing unique address information. These routers function as switches in a local network. They examine the destination IP address once they reach the final endpoint.
Essentially, the Layer 3 header analysis occurs only once: upon the packet entry into the MPLS domain. This approach potentially leads to faster transmission compared to traditional packet-switching networks.

Benefits of Our MPLS Services
MPLS services at Promwad include using advanced label switching technology to improve the performance, security, and manageability of data traffic. Discover the benefits of using MPLS in the telecom industry:

Powering enterprise networks
Since its release in 2001, MPLS has been a reliable telecommunication technology to power enterprise networks. Its primary purpose lies in connecting remote workers or branch offices with applications and other data located in a data centre of an office or headquarters.

Fast and reliable packet delivery
While general internet traffic usually takes more overloaded paths without compromising performance, voice data or video requires a low-latency routing. This technology saves valuable router resources, providing reliable and fast packet delivery crucial for real-time or high-performance applications.
Supported Applications
Promwad Drives MPLS Development
MPLS functionality for Microchip switches
We tested it on the VSC7558 development board by Microchip. MPLS operates on the Sparx-5 switches family.
SDK: Microchip IStaX.
SD-WAN: Emerging Alternative to MPLS?

The industry has seen the rising interest in software-defined WAN or SD-WAN and its adoption acceleration over the past few years.
The primary reason is that SD-WAN architecture is optimised for cloud computing. According to Gartner's 2020 Magic Quadrant for Wide Area Network Edge Infrastructure, by 2024, 60% of enterprises will have implemented SD-WAN, compared to about 30% in 2020. This trend is driven by the need to enhance agility and support for cloud applications. The COVID-19 pandemic and the widespread shift to remote work have further accelerated this trend.
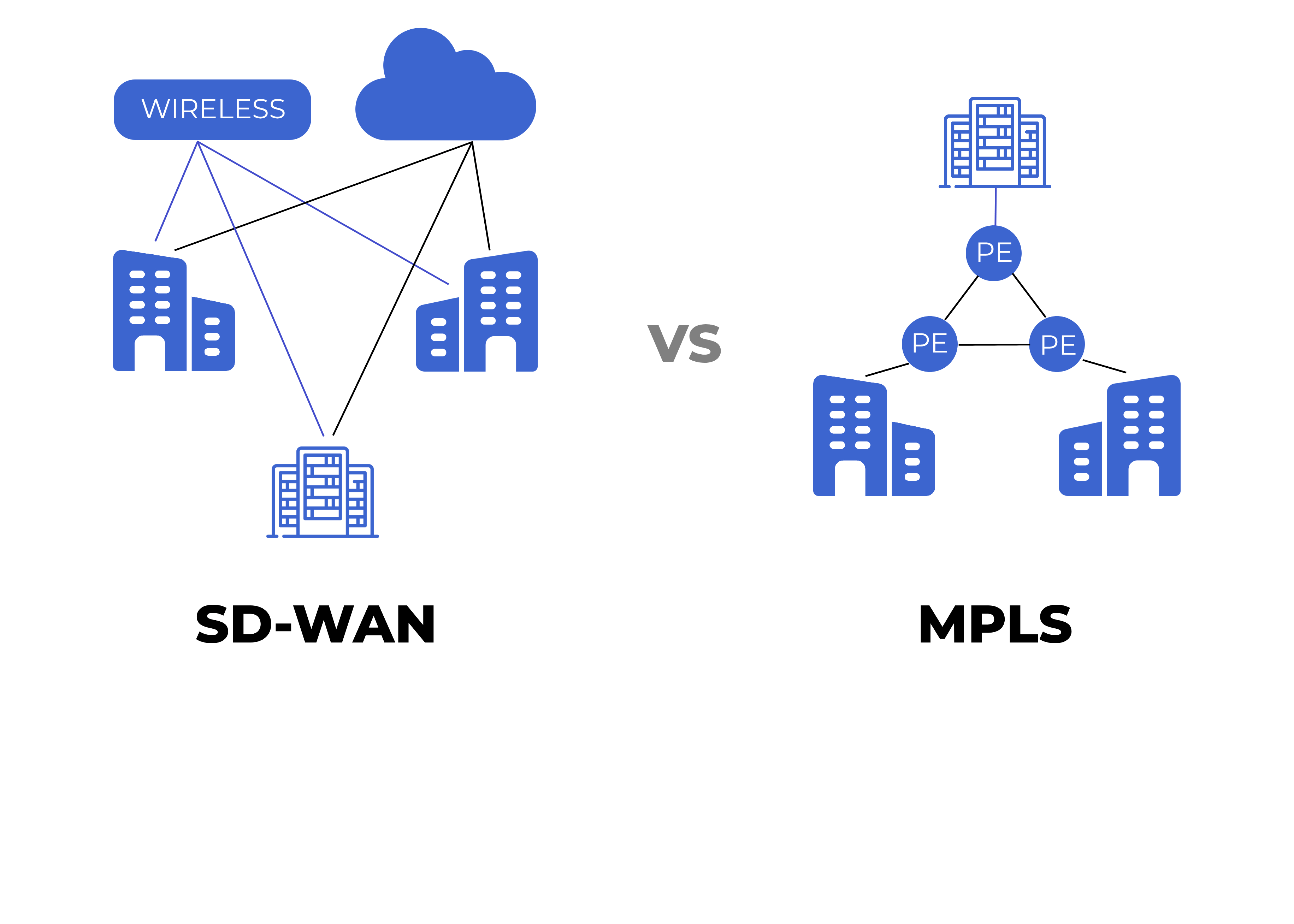
Although SD-WAN vendors tend to consider their solution as an «MPLS killer», it cannot fully replace MPLS networks. Instead, MPLS and SD-WAN are complementary technologies. The decision criteria for choosing between them primarily include costs, centralised management requirements, and the needs of mission-critical applications. Nonetheless, MPLS will continue to play a crucial role as a foundational component of enterprise WANs.
Our Case Studies in Telecom
Would you like to implement MPLS functionality for Microchip switches?
Please, drop us a line. We will contact you today or next business day. All submitted information will be kept confidential.
FAQ
Where does MPLS fall within network layers?
MPLS can create end-to-end paths that act like circuit-switched connections but deliver IP packets. The protocol allows IP packets forwarding at Layer 2 (switching or data link level) without being passed up to Layer 3 (network level). That is why MPLS is also known as a Layer 2.5 protocol.
Where is Multiprotocol Label Switching used?
While the hybrid MPLS & SD-WAN approach is gaining momentum for large Tier-1 companies, MPLS will remain a tool for mid-size businesses. Application areas include connecting large regional offices, manufacturing sites, and retail facilities with point-of-sale systems.
What are sub-parts of the MPLS label?
MPLS label consists of the following parts: the label; experimental bits for setting the priority of labelled packets; bottom-of-stack, which states that this particular router is the last on the route; and time-to-live, specifying the number of hops for a packet until it is discarded.








