Microelectronics is experiencing another phase of a rapid development, and this is largely due to a rapid development and implementation of new hardware components. Thanks to advanced microprocessors with well-developed peripherals and flexible possibilities, so-called "systems on chips", a real revolution took place in digital equipment area.
The market raises new requirements for all electronic products, both for functional and technical parameters. In order to conquer in that uneasy competition modern electronic devises must have the following:
- a unique set of features
- an advanced user interface
- high performance of the underlying platform which allows to upgrade the device
- embedded operating systems
- low power consumption
- embedded high resolution LCD displays
- an ability to connect to the Ethernet, including with the use of PoE
- an ability to store large amounts of data in non-volatile memory and on external storages
- a complete set of standardized wired and wireless interfaces.
To implement these requirements in a single electronic device is possible by using the system on a chip (see. the image below). Today, the market represents a great variety of finished chips, as well as solutions that can be integrated in the FPGA from leading manufacturers: Intel, Freescale, Texas Instruments, Marvell, Analog Devices, Altera, Atmel, NXP, Xilinx, Cirrus Logic, RDC, Cypress, Sharp, Net Silicon etc. Device development based on such chips opens new opportunities.
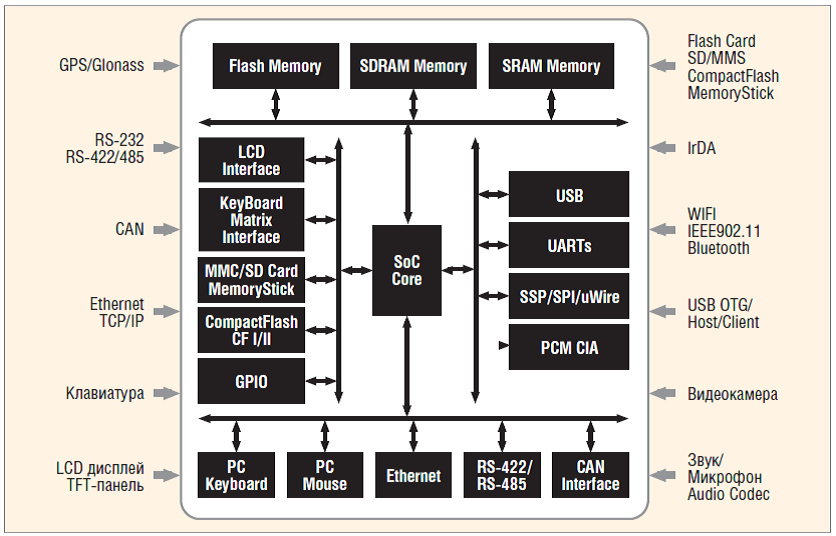
WHAT IS A “SYSTEM ON A CHIP”?
A system on a chip, and its application in electronics development
A system on a chip (SOC) usually contains a high performance processor core and a large set of peripherals which we are used to see in PCs and in modern mobile devices. A typical based on SOC embedded system contains the following interfaces and controllers:
- a system bus and LPC / ISA, PCI, PCMCIA bus controller
- NOR/ NAND Flash, SDRAM, SRAM, DDR controllers
- an Ethernet controller
- UART, SPI/SSP/uWire, RS 232, RS 422/485, CAN serial interfaces
- WiFi/IEEE802.11, ZigBee, Bluetooth, IrDA wireless interfaces
- Flash card memory SD/MMC, CompactFlash and Memory Stick interfaces
- an STN/TFT/OLED controller
- a matrix keyboard controller
- GSM / GPRS, CDMA, etc. wireless data transmission modules
- modules to receive signals of GPS and Glonass satellite navigation systems
- hardware support for floating-point, encryption, DRM etc.
- interfaces for audio and video signals.
SOC CLASSIFICATION
SOC review for electronics development
A large number of vendors and “unlimited” variety of chips bring certain disorder when selecting an elements base to implement this or that device. There are a number of features to categorize SOCs:
- by the processor core: ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, x86, and others
- by core performance and system bus frequency
- by set of interfaces
- by cost of the chip and a minimum binding
- by positioning of the chip by its manufacturer
In addition, design engineers have to take into account SOC availability, a planned production cycle of the chip, purpose and operational features of future products, soldering and PCB technology, completeness of documentation, tech support etc. In a situation like that, even a qualified specialist may make a solution which is not optimal. The suggested classification is formed on the basis of completed projects (taking into account chips availability) and is designed to help Russian developers of finished products.
SOC classification by application
Standard solutions may be implemented with SOC from the following classification groups:
- or budgetary use
- for the remote control devices
- for terminal devices
- dual core, for data processing
- for FPGA based specialized computers
For budgetary applications
SOC of this group can be used in onboard electronics, in management and access control systems, in warning systems, in industrial controllers, and in outputs of audio information. Chips can be used in projects that do not require large amounts of software code or operating systems use.
A chip of this group is characterized by its low cost (up to $ 10.00), simple circuit design of the final product (does not require external memory, low frequencies of bus data exchange), and ability to be implemented on device with a two-layer PCB, easy installation, debugging and testing. These SoCs are descendants of microcontrollers and they inherit their peripherals (GPIO, UART, I2C, SPI, ADC / DAC, PWM), but they have a more productive ARM7 core and SoC-specific interfaces (USB, LCD, Ethernet).
SoC for remote control devices
It is reasonable to use the chips of this group in products which perform remote control using Ethernet or wireless interfaces, i.e. in data collection devices, in controller hardware servers, and in network equipment (access points, gateways, routers). High performance core allows using operation systems with file system support, a TCP / IP protocol stack, an FTP-server and a web-server. Such chips cost $10.00-20.00; they have medium complexity of circuit design (connection to memory chips and implementation of physical layer interface are needed), a device can be implemented on a PCB with 4 - 6 layers.
SoC for terminal devices
(electronics development based on low cost SOC)
Chips of this group are suitable for electronic devices with built-in high resolution LCD matrixes. As final products may be tablet and panel computers, measurement instruments, on-board computers with high-resolution screens, medical monitors and terminals, information kiosks and panels.
Microchips of this group are quite expensive, $20.00-30.00, but they justify their use due to the high degree of modern interfaces integration. Therefore, developed circuit design has a medium complexity: a PCB can be made with 6 - 8 layers, and in most cases installation of BGA type enclosures may be required.
A developer provides timely execution of each stage and informs its customer about the progress of stage fulfillment. In the end the developer will bear a full responsibility for performance of the final device, which will relieve the customer from the risks associated with time and money losses when the customer’s development team fails to complete the project.
Double-core SoC for data processing
Chips of this group are perfect to be applied in devices that require parallel data processing or information gathering with its simultaneous display. Devices that may require such features are completely different: from multimedia to the measuring equipment. For example, in measuring equipment it is often necessary to carry out convolution using a DSP core and simultaneous information displaying on the LCD, as well as signal processing from a keyboard. OMAP5912 processor equipped with DSP and ARM cores with a common system bus can successfully complete this kind of task. Microchips of this group are suitable for a variety of mobile devices due to their low power consumption.
Cost and other characteristics of this SoC group are similar to those of the previous group, but there is one significant difference: it is the work with a dual-core architecture when writing and debugging embedded software.
SoC for specialized FPGA based computers
Of course, flexible FPGA based solutions are popular among developers (see. Table 5), but their application is justified in implementation of parallel processing algorithms, high-speed processing streams algorithms, in a set of unique or specific interfaces, integration of different nuclei and digital signal processing algorithms in one device.
FPGA application makes development process more complicated and increases the cost of a final product. The big advantage of the FPGA is configurability, which allows even a small engineering firm to have 1 or 2 platforms and develop various products on their base.
CONTRACT DEVELOPMENT AND DESIGN SERVICES BASED ON SOC
With all SOC advantages, we should not forget that a product development process on a such elements base is very laborious and requires not only competent professionals in one’s staff, but also a great responsibility.
Projects with the use of SoCs cannot be made on a kitchen table by one or two developers, as one has to go through a number of laborious steps:
- to select architecture
- to select the element base, taking into account its cost, availability and compatibility
- to develop a schematic diagram with a large number of links
- to trace a circuit board with high mounting density
- to verify the circuit and PCB trace
- to organize production of prototypes in a reliable company
- to carry out the primary PCB bring-up
- to develop test software and, if necessary, additional hardware, and software monitoring as well
- to prepare a comprehensive Board Support Package (BSP), which includes: a primary loader with peripherals and memory test software, an operation system, interface and device drivers installed in the PCB, system utilities, automatic scripts and packages for software assembly
- to develop application and user software, and user interfaces
- to conduct integration tests of the product
- to prepare the design documentation and instructions for installation, firmware, testing and programming the device
- to make an initial batch of the products and prepare the product for mass production (it is a separate laborious time-consuming stage of the work)
Product development requires solving an entire complex of tasks with participation of managers, marketers, system engineers, programmers, developers, designers and other experts. In this situation, using contract development services is greatly important, since a company engaged in applying SOC, will perform product development faster and better than a team of engineers which is not specialized in this area.
In electronics development project, an outsourcer takes upon himself a number of obligations to accomplish all project stages: electronics, circuitry, boards, enclosures, interfaces, and software; as well as manufacturing the final device.
Attraction of highly qualified experts with narrow specialty, budget transparency, development timing, application solutions which were tested and used in other projects and industries explain the effectiveness of contract development very well.
In many cases, it is more profitable for a manufacturer to transfer product development to a contract developer, and focus its own efforts on market research and product promotion. Therefore competent use of contract development services can provide a new level of product quality and reduce their time to enter market.
The classification presented in the article is based on real experience of application of those SOCs in successful products which were ordered to design by Promwad.
