Industrial Trends 2024: Сloud-Based Solutions, Advanced Security and Metaverse

What industrial solutions should you invest in and include in your long-term strategy? As we support our clients worldwide with the development of advanced software and hardware solutions, we couldn't help but spot the latest trends in industrial automation that are driving the market forward.
Seven industry drivers
1. IT/OT convergence: virtual PLC and IIoT integration
2. Convergence of communication technologies
3. Cloud and analytics integration
4. Increased system safety: SIL 3 software compliance
1. IT/OT convergence: virtual PLC and IIoT integration
As the industry seeks to optimise production equipment hardware costs, there is a marked shift towards server infrastructure consolidation. Supplemented by real-time servers, local servers within factories are becoming the main part of industrial networks.
An important aspect of this trend is the transition of all sensors and drivers to the Ethernet physical layer (protocols like Ethernet APL and Ethernet SPE). The controller level is disappearing, and being replaced by virtual PLC, which is part of local servers at factories.
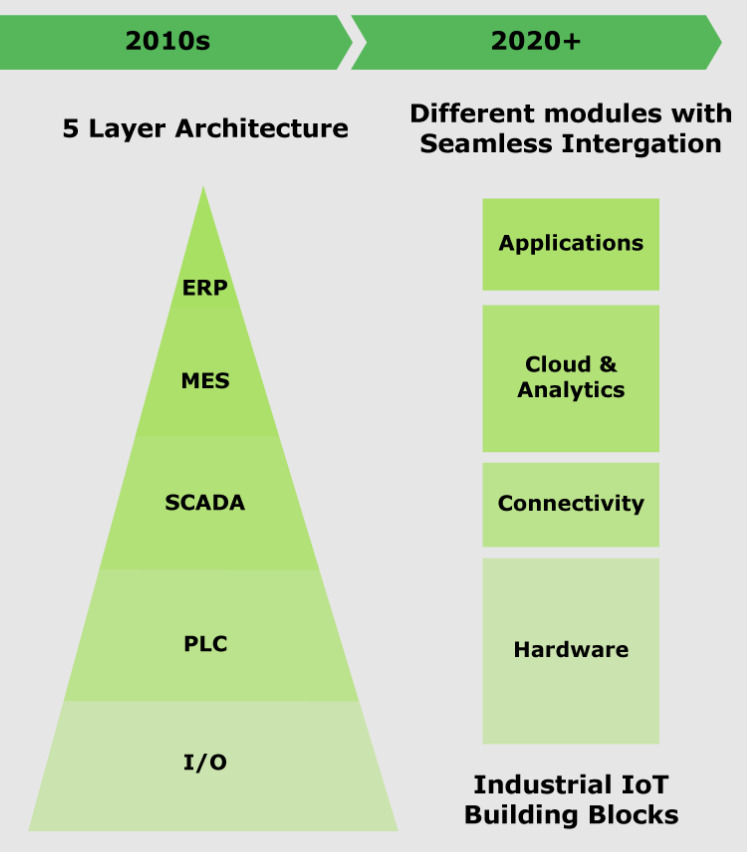
IT/OT convergence: transition from a 5-level to a 4-level architecture
A virtual PLC runs in a virtual environment with containers and hypervisor technologies instead of hardware. To deploy or orchestrate virtual PLC, users can choose any local server.
Traditional electrical signal standards such as 4-20 mA, 0-20 mA, 0-10 V and others are disappearing from the market, making way for more efficient Ethernet-based communication solutions. PROFIBUS is widely replacing PROFINET, and technologies such as IO-Link are on the verge of transitioning to IO-Link Ethernet, albeit with a greater inclination toward PROFINET.
According to Codesys experts, in Industry 5.0, OT and IT are completely merged. Instead of purchasing and installing multiple controllers, it is sufficient to load the existing IT platform on the network with virtual controllers and manage them centrally.
2. Convergence of communication technologies
The evolution of communications in industrial automation follows the standardisation, interoperability and integration of industrial Ethernet and real-time communications protocols. This trend is characterised by the adoption of advanced networking technologies such as PROFINET, CC-Link, EtherNet/IP and TSN for industrial applications.
TSN Industrial meets industrial automation requirements, where precise synchronisation, reliability and determinism are critical. TSN IA technology helps industrial networks achieve high levels of synchronisation and ensure timely data delivery. TSN is the underlying technology for communication standards such as PROFINET TSN, EtherNet/IP TSN, Sercos III TSN or CC-Link IE TSN.
- PROFINET is known for its versatility and reliability. Its high-speed capabilities and real-time data exchange are well-established in various industrial environments.
- CC-Link was developed to meet the requirements of high-performance applications. This protocol supports large-scale networks and operates with different types of devices in critical processes.
- EtherNet/IP, with its open and interoperable architecture, integrates seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure, simplifying deployment and management while ensuring secure communication between devices from different vendors.
3. Cloud and analytics integration
Industrial cloud solutions are changing the industry, focusing on analytics and predictive maintenance based on a robust server infrastructure supported by the necessary security measures.
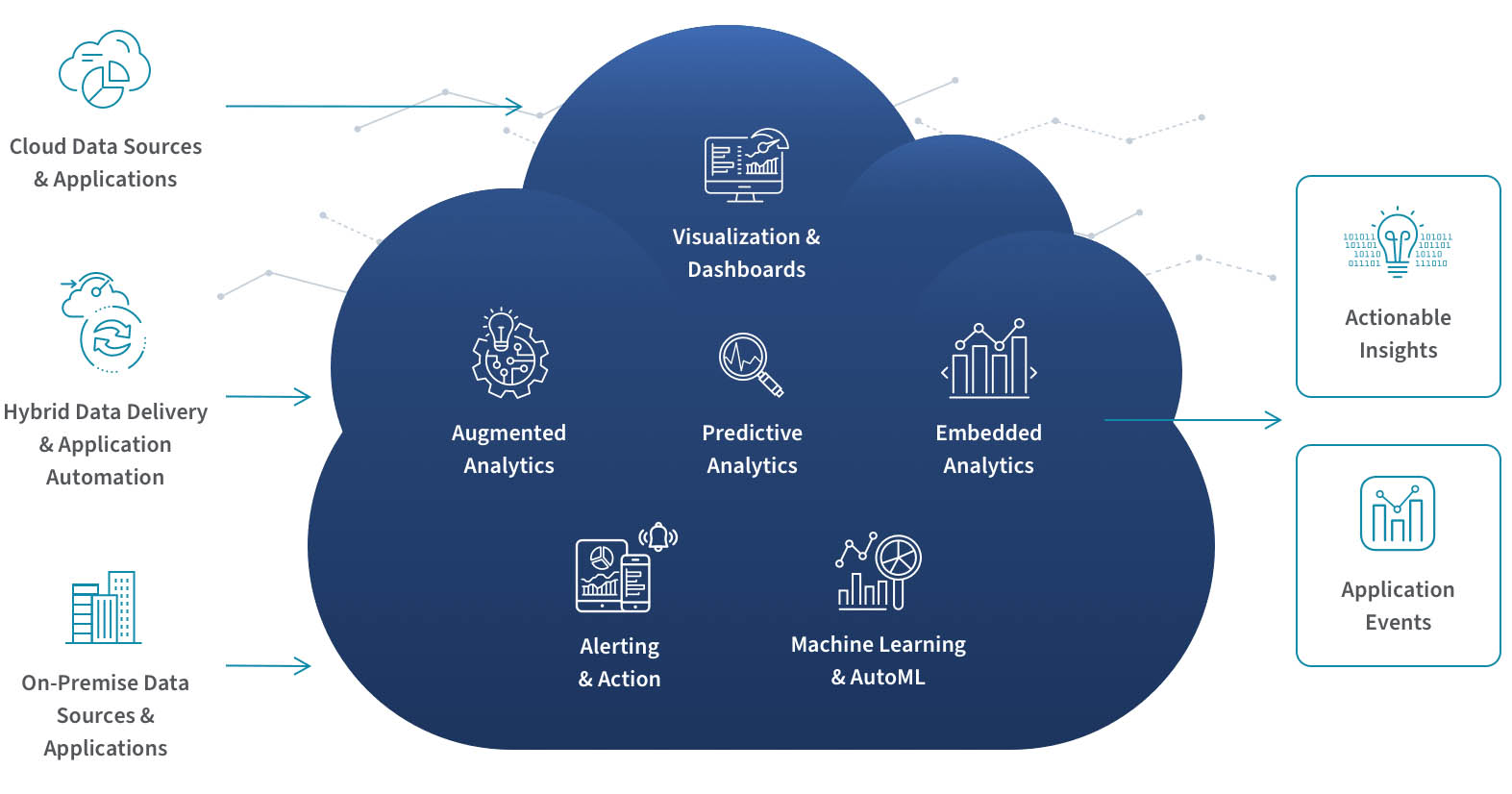
Сloud-based data analytics and BI processes on vendor-managed infrastructure. The solution by QlikTech as an example
The distinctive feature of Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 is the spread of devices interconnected within the cloud ecosystem for real-time monitoring, analysis and decision-making.
4. Increased system safety: SIL 3 software compliance
Safety Integrity Level 3 (SIL 3) is defined by the IEC 61508 standard issued by the International Electrotechnical Commission to measure a safety system's effectiveness in reducing hazardous events.
In practical terms, SIL 3 represents a high level of safety system integrity. The software, subjected to a safety lifecycle, verified and validated, achieves SIL 3 compliance through independent assessment by certified organisations. This approach is critical for industries where the consequences of a failure could result in serious personal injury, major equipment or environmental damage.
The increasing demands on safety are embodied in the appearance of software tools such as the SIListra Safety Transformer and CODESYS Virtual Safe Control. SIListra automatically embeds coded processing into the source code of a complete application written in C and C++.
CODESYS Virtual Safe Control is a software solution that simulates a safety controller. It monitors and controls equipment, ensuring operates safely according to defined standards without using physical safety equipment. It tests and verifies the safety functions of machines and systems in a simulated environment.
5. Predictive maintenance on local servers
Predictive maintenance and edge AI have traditionally relied heavily on hardware. However, advances in software technology have made them increasingly software-centric. Algorithms for predictive maintenance are being deployed on local servers. This transition enables better integration with cloud systems and provides access to extensive computational resources, which greatly enhances the efficiency of the predictive maintenance process.
The new approach helps businesses reduce costs because the need to produce physical hardware is minimised. While some aspects of predictive maintenance may still require hardware, the bulk of the process – particularly data analysis and operational tasks – is moved to local servers located at industrial sites, ensuring that the maintenance can be efficiently performed near the equipment and processes it monitors.
6. Digital twins
The concept of creating a digital twin of a factory, where every aspect of the physical environment is mirrored in a virtual space, provides businesses with great opportunities to optimise operations. From tracking pallet movements to monitoring the location of personnel and measuring critical parameters such as voltage levels, a digital twin can recreate a variety of operations.

A digital twin developed by Promwad based on Xilinx Kria SoM
Digital twins also enable predictive maintenance to troubleshoot equipment and minimise downtime quickly.
Read our case study: Digital Twins Design for Control Loops in Industrial Networks
7. Industrial metaverse as a game-changer
The industrial metaverse reflects and models real-world systems. It uses technologies such as digital twins, AI, augmented reality, blockchain, cloud and edge computing to create a link between the real and digital worlds.
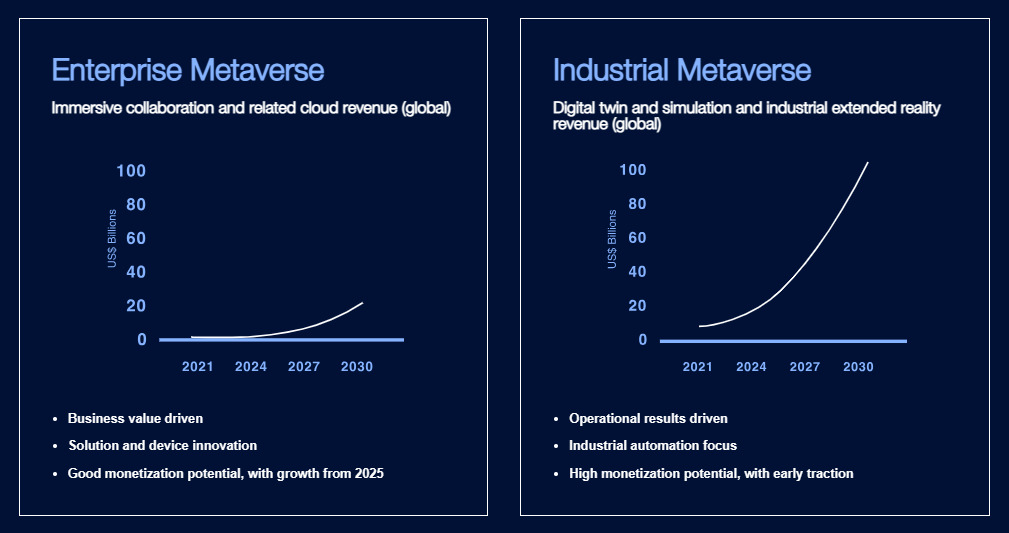
Enterprise and Industrial Metaverse: Monetisation Potential in Billions of US dollars from 2025. Source: ABI Research, Evaluation of the Enterprise Metaverse Opportunity, Third Quarter, 2022
This metaverse has the potential to transform workflows and bring significant benefits to business and society. By allowing businesses to model, prototype and test design iterations in a physics-based environment, the industrial metauniverse enables real-world problems to be solved digitally.
The industrial metaverse includes three layers:
- Digital twin is the main block of the industrial metaverse. Physics-based copies look like and behave like virtual representations of anything.
- Software-defined automation combines the real and digital worlds, describes what happens on production machines. Today, PLCs speak industrial programming language; the next generation is Virtual PLCs.
- Data and AI. In metaverse raw numbers become actionable insights with the help of edge devices and AI. Edge devices filter the data and collect only important, and AI allows access to all the knowledge for better engineering.
Key capabilities and ecosystems for the metaverse are still emerging, including connectivity, computational power, digital twin fidelity, interoperability, privacy, and security.
NVIDIA Omniverse is one of the most interesting technologies contributing to the industrial meta-universe. Omniverse is a real-time 3D design collaboration and physically accurate modelling platform. It enables engineers, designers, and other professionals to collaborate in shared virtual spaces to create detailed simulations of real-world environments and processes. It can design factories, simulate workflows, or train artificial intelligence models in a virtual space that mirrors the physical world.
The industrial automation trends in 2024 represent a movement towards greater connectivity, efficiency, and innovation. As these trends evolve, businesses need to stay ahead of the game and take advantage of the opportunities presented by them.
Promwad is committed to working with companies to harness the power of these trends and drive industrial automation into the future. Our engineering team is ready to partner with you, using our experience and knowledge to co-create innovative solutions for your business.
Let's build the future together! We are ready to discuss your ideas in the field of industrial automation: